Nerve Damage in Diabetes and the benefits of EMG/NCS Studies
Nerve Damage in Diabetes and the benefits of EMG/NCS Studies
Nerve Damage in Diabetes and the benefits of EMG/NCS Studies

Diabetes, especially if uncontrolled, can cause damage to the nerves of the body. This damage occurs due to decreased blood circulation to the nerve tissue and due to the high blood sugar levels. The condition is called diabetic polyneuropathy since it affects multiple nerves of the body. It usually develops 10-20 years after the initial diagnosis.
Diabetic neuropathy can damage not only peripheral nerves in the extremities (hands and feet) but also cranial nerves and nerves to vessels and organs of the body (autonomic neuropathy).
When it comes to the nerves of the hands and feet the condition will cause decreased sensation but also numbness and tingling. Many patients suffer burns in their hands because they cannot feel the hot stove or injuries in their feet because they may not feel a sharp object when they step on it.
Eventually, the condition may affect motor nerves and cause weakness on the muscles of the feet and hands.
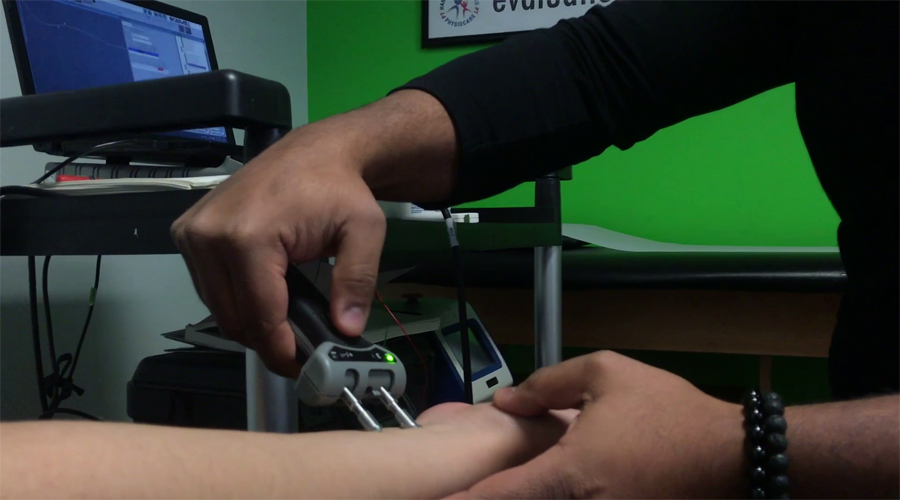
Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) can be a very useful tool to identify the neuropathic changes and quantify the severity of the condition. EMG/NCS is a very easy test and can be performed in about an hour. The specialist performing the test uses mild electrical impulses on the examined nerve to evaluate the ability of the nerve to conduct the change in potential along the nerve. Also a small pin may be used to evaluate the integrity of the examined muscles.
Long term control of the diabetes along with pharmacotherapy, proper nutrition, exercise and vitamin supplementation may help improve the neuropathic changes and this improvement may be evaluated by EMG/NCS testing.